~ Salumanus sheds light on the on the unconventional ways in which fibre optics are used ~
The global fibre optics market encompasses a broad range of applications beyond telecommunications, extending into space, healthcare, security and more. As of 2024, the fibre optic cable market size is estimated to be USD 12.83 billion and is expected to reach USD 19.26 billion by 2029, according to Mordor Intelligence. Here, Marcin Bała, CEO of optical network solutions specialist Salumanus, explores the less talked about applications of fibre optics.
Fibre optics operate on the principle of total internal reflection. This technology uses strands of glass or plastic fibres as a medium to transmit light signals over long distances. The core of the fibre is surrounded by a cladding with a lower refractive index, which ensures that light introduced at one end of the fibre is kept in by bouncing repeatedly off the internal walls of the fibre, despite bends along its path.
These light signals represent data, which can be anything from telephone conversations to internet content. The efficiency of fibre optics lies in their capacity to carry a large amount of data at the speed of light, with minimal loss of signal over long distances.
Fibre optics in space
Fibre optic sensors offer several advantages for spacecraft monitoring and control due to their small size, immunity to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ability to function across a wide temperature range. These sensors are integrated into spacecraft for monitoring structural integrity, temperature and pressure, enhancing their safety and performance in the harsh conditions of space.
According to Frontiers, the European Space Agency has used fibre optic sensors for over two decades, exploring their potential in both launcher and satellite applications. These applications range from cryogenic environments to high-temperature re-entry scenarios, demonstrating the versatility and reliability of fibre optics in space.
Fibre optics in healthcare
Fibre optics play an important role in minimally invasive surgeries (MIS) by allowing surgeries to be performed through tiny incisions, significantly reducing recovery times and improving patient outcomes.
The paper Biomedical application of optical fibre sensors explores how fibre optic endoscopes, for example, provide high-resolution images from inside the body, aiding in diagnostics and surgical procedures without the need for large incisions. This technology sees use in gastroenterology, urology and pulmonary medicine, where internal visualisations are essential for diagnosis and treatment.
Fibre optics are also instrumental in photodynamic therapy (PDT), where light-sensitive compounds are activated using light delivered through optical fibres to treat cancers and other diseases, as explained in Optical fibres and sensors for biomedical applications. This technique allows for targeted treatment, minimising damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
Similarly, fibre optics are used in laser surgeries for precise cutting and ablation, offering a less invasive alternative to traditional surgeries with reduced healing times and complications.

Fibre optics in security
Fibre optic sensors aren’t only useful in space but have found promising applications in security, especially in physical intrusion detection systems. These sensors, due to their inherent benefits like immunity to EMI and suitability for monitoring harsh environments, are increasingly being used to secure both commercial and residential premises from physical security breaches.
According to IEEE Sensors Journal, optical fibre-based techniques for sensing, interrogation and networking have been developed to detect unauthorised access with high sensitivity and specificity. These systems can protect perimeters, fences, windows and doors, offering a modern solution to physical security challenges.
These are just a handful of examples of how fibre optics are used in applications other than telecommunications, demonstrating their usefulness and diversity.
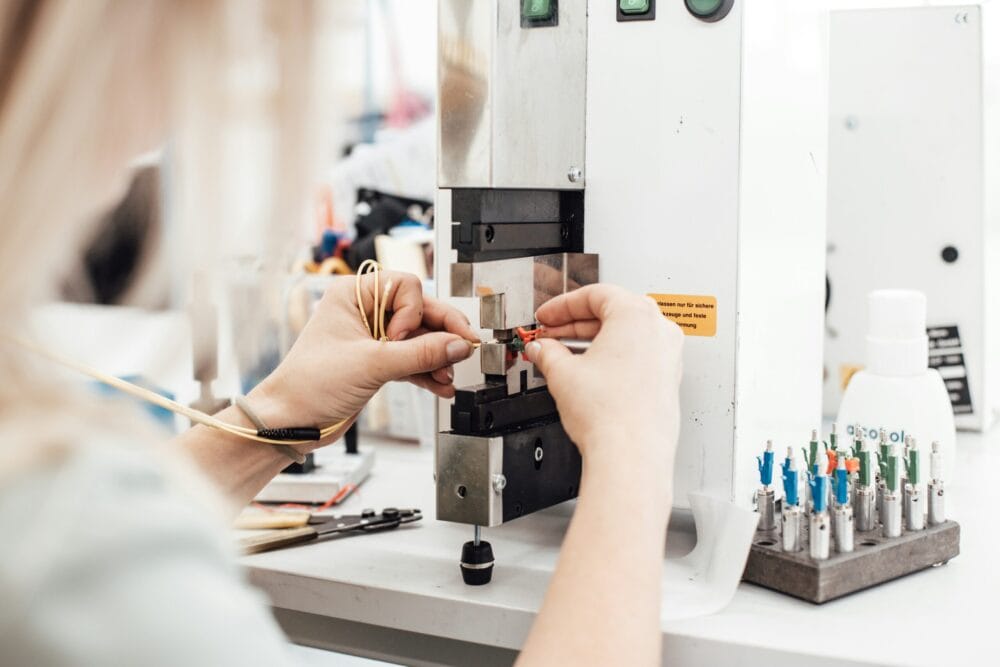
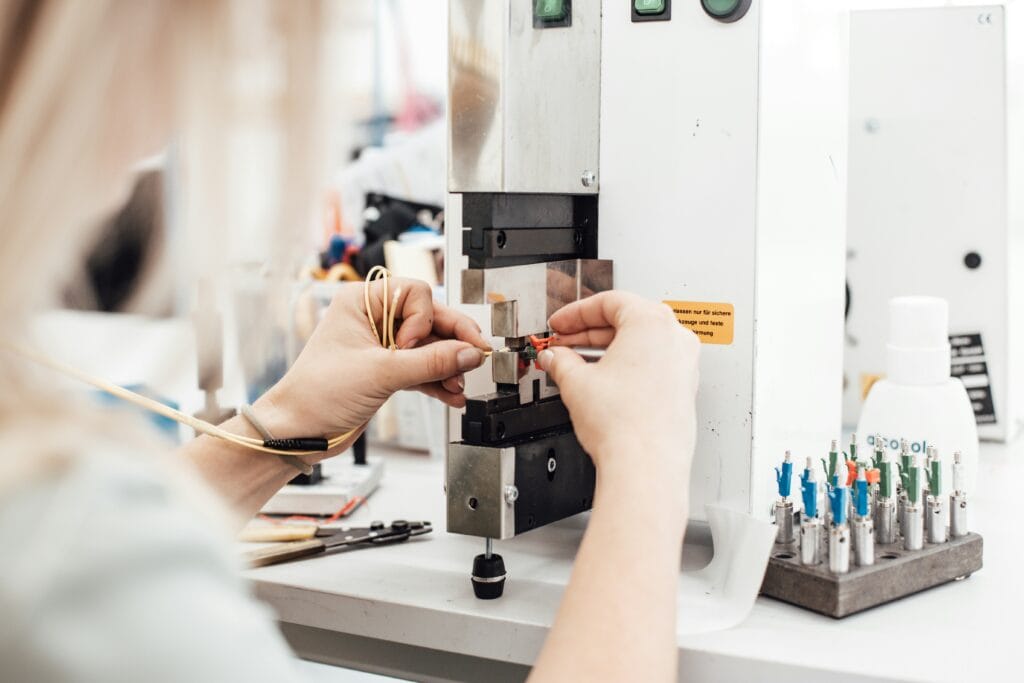
Salumanus has a wealth of experience with fibre optics, specialising in enhancing the functionality and efficiency of fibre optic networks. Its universal optical transceiver is a device that converts electrical signals to optical signals and vice versa. This technology is used for the transmission of data over fibre optic cables, facilitating high-speed internet connections.
To find out more about how optical transceivers work, visit Salumanus’ website https://www.salumanus.com.