How bottles & jars are changing the face of Civil Engineering projects and the testing needs behind it.
How many tonnes of recycled glass would it take to build an emergency support for one of the busiest four lane highways in the world? I honestly wouldn’t have a clue but I know someone that does.
Theresa Andrejack is the Chief Technical Officer for AERO Aggregates, a Philadelphia based company with a further plant in Florida and another in California coming on stream later this year. The company takes your empty bottles and jars from recycling plants and landfill sites, turning them into an eco friendly aggregate for use in a myriad of civil engineering applications.
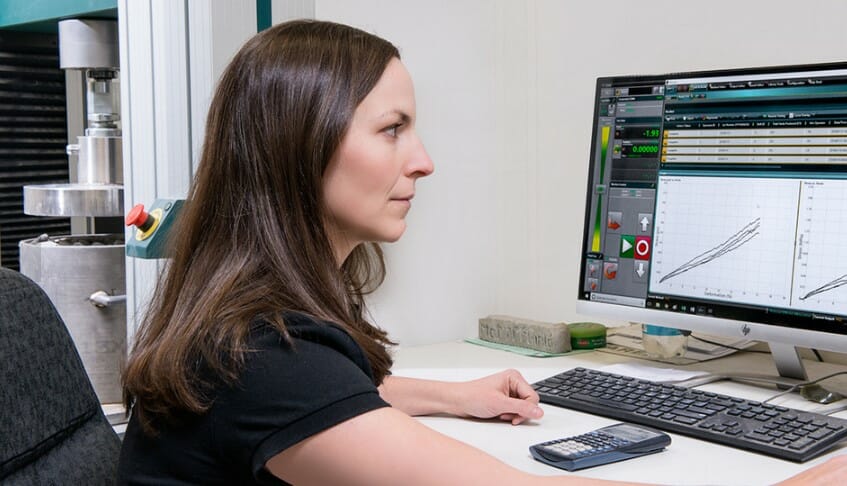

Theresa Andejack, Chief Technical Officer at AERO Aggregates, undertaking tests on the glass based FGA on a Tinius Olsen 150ST
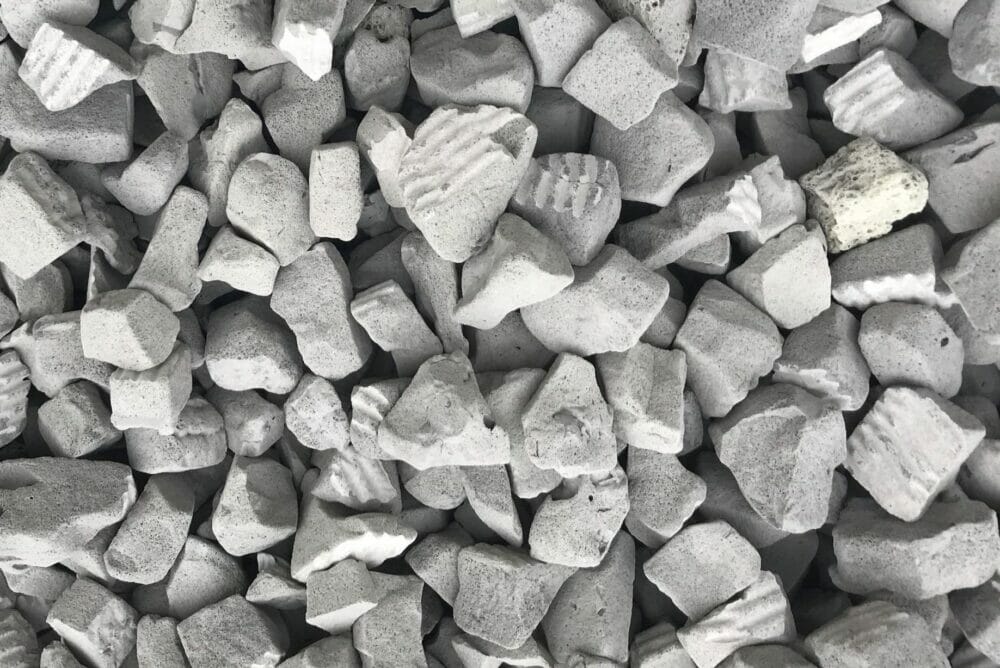
Foamed Glass Aggregate has been used as backfill in numerous projects, primarily where the soil underneath is soft and compressible and cannot support too much excess weight, such as an overnight parking apron for airplanes at Philadelphia International Airport.
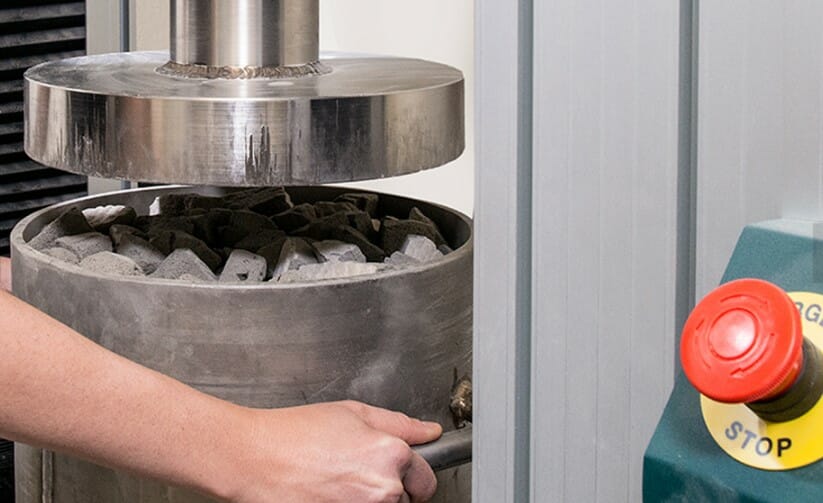

Foamed Glass Aggregate undergoing compression testing at the AERO Aggregates testing lab
In fact, it is so effective that it is being used to build up the damaged section of the Cottman Avenue exit ramp on the I-95 interstate on the outskirts of Philadelphia, which collapsed following a tanker fire in June this year. FGA will be used to support a temporary, six-lane highway while contractors rebuild the actual bridge.
“FGA is absolutely ideal for this project as it only weighs around one sixth of regular soil due to it being full of air bubbles. In the case of I-95, this will help protect the ageing sewage lines running underneath the structure as they simply couldn’t withstand the weight of another 20ft of the soil material,” said Theresa.
“It was an awful accident and has caused huge inconvenience to everyone in the Philadelphia area so we’re just delighted we can help and get things moving again extremely quickly.”
The manufacturing process of the aggregate starts with grinding glass into a powder and subjecting it to a three-phase cleaning and filtering procedure. Workers then add a proprietary, mineral-based foaming agent and heat the powder in a kiln at 1,650 degrees Fahrenheit.
The material emerges from the kiln looking like a long, gray sheet of cake. Upon cooling, the material cracks into gravel-like pieces and is further broken down in a tumbler into one to two-inch chunks.
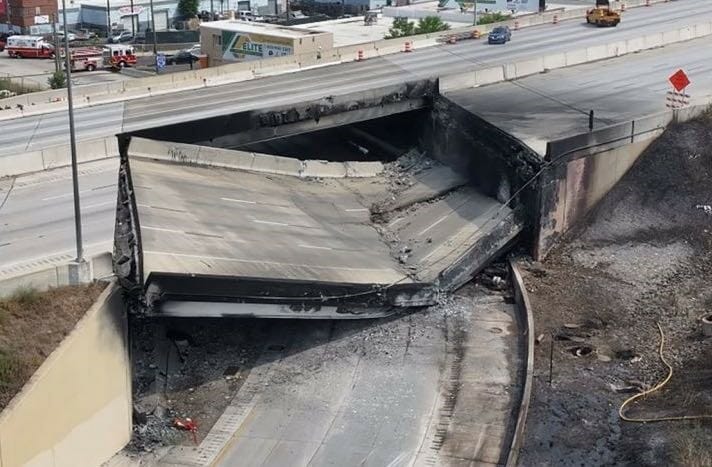

The I-95 collapse on the outskirts of Philadelphia following a truck fire on the highway
“We aim for the bulk density of our standard product to not be any heavier than 15 pounds per cubic foot, which corresponds to about 240 kilograms per cubic meter. We follow ASTM C29 standard for this type of bulk density measurement.”
“The other test that we run on a daily basis is a confined compressive strength test, which is what we use our Tinius Olsen 150ST machines for in each of our Philadelphia and Florida plants, with one on order for California. The company’s experience and input has been invaluable in developing the product from the get go and being a local company to ourselves has been an even bigger bonus.”
“The test method used for these compressive tests is EN 1097-11 although we’ve started down the road of trying to get this test standard in place at ASTM, which will obviously take some time.
But where does all the required glass come from?
“Most communities do have some type of recycling program in place. Sometimes the trend in recent years has been that some communities have dropped glass from the materials that they’re collecting but certainly there’s still many programs that do collect glass.”
“We work with those local programs for our plants to source the product and we can take what is really the lower value glass because it’s the mixed color, the smaller pieces that generally can’t be used by a bottling operation or even a fiberglass operation so it’s fairly low value material.”
“When our California plant opens later this year, we will have the capacity to divert over 500 million bottles per year from landfill.”
It’s been an amazing journey for AERO Aggregates and a perfect example of how materials testing is vital to the development of any exciting new product. This is especially true with FGA, which can make such a huge difference to everyday life and Tinius Olsen look forward to helping develop this material even further in the future.
Oh and it will take and estimated 2,000 tonnes of FGA to build the supporting structure for the I-95 exit ramp.
That’s a lot of glass bottles…………
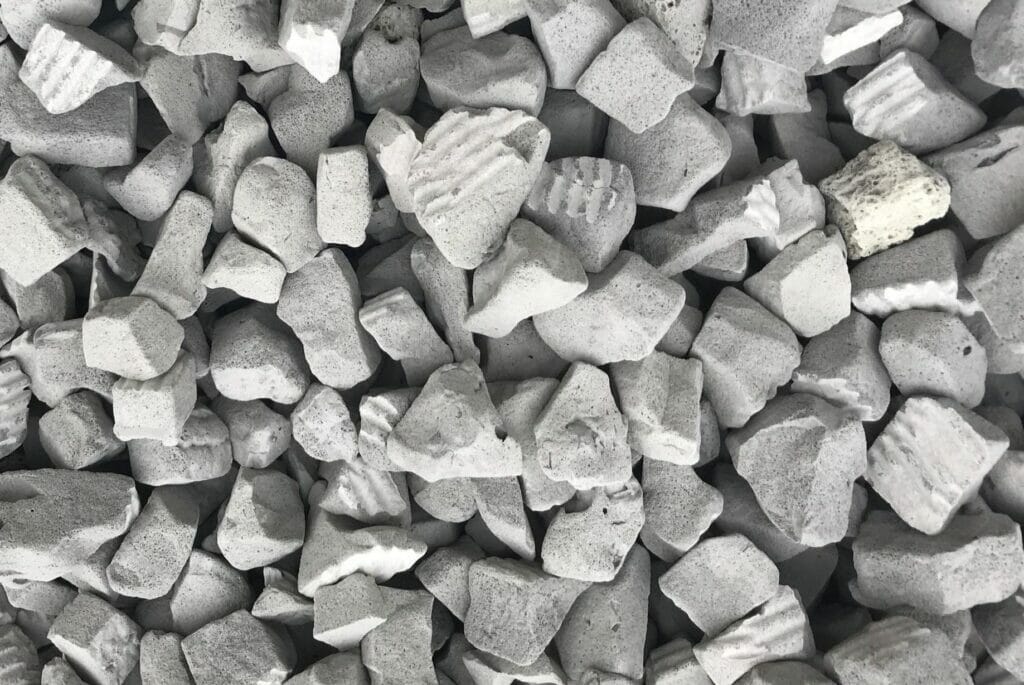

The manufacturing process of the aggregate starts with grinding glass into a powder and subjecting it to a three-phase cleaning and filtering procedure. Workers then add a proprietary, mineral-based foaming agent and heat the powder in a kiln at 1,650 degrees Fahrenheit